«Το κρασί, αν χρησιμοποιηθεί κατάλληλα και με μέτρο,
ανάλογα με τον άνθρωπο, είναι άριστο τόσο για την υγεία, όσο και για την
αρρώστια»
Ιπποκράτης, 460-377 π.Χ., Πατέρας της Ιατρικής
Ένα γνωμικό το οποίο επιβεβαιώνεται τα τελευταία χρόνια μέσα απο τα
αποτελέσματα πολλών ερευνών πάνω στην θετική επίδραση της μέτριας
κατανάλωσης αλκοόλ στη λειτουργία του οργανισμού. Βέβαια, κάθε ποσότητα
πάνω από τη συνιστώµενη, σε συνδυασµό µε τη χρόνια κατανάλωση -
εξάρτηση, µπορούν να προκαλέσουν πολύ σοβαρά προβλήµατα υγείας και να
οδηγήσουν μέχρι και στο θάνατο.
Ποιο είναι είναι όμως το ταξίδι του αλκοόλ στο σώμα μας; Ποια
διαδρομή ακολουθεί και ποια όργανα επηρεάζει θετικά ή αρνητικά;
Είναι γνωστό ότι η υπερβολική κατανάλωση αλκοόλ προκαλεί σοβαρά
προβλήματα στο ήπαρ και οδηγεί σε πολλές περιπτώσει σε κίρρωση του
ήπατος. Αλλά το συκώτι μας δεν είναι το μοναδικό όργανο που
καταστρέφεται από το αλκοόλ.
Σύμφωνα με το Εθνικό Ινστιτούτο Αλκοολισμού και Κατάχρησης Αλκοόλ των
ΗΠΑ, οι επιπτώσεις του αλκοόλ στον οργανισμό μας ξεκινούν μόλις 10
λεπτά μετά από την πρώτη γουλιά ποτού που θα πιούμε. Ωστόσο, είναι οι μακροπρόθεσμες επιπτώσεις του αλκοόλ εκείνες που θα πρέπει να μας ανησυχούν περισσότερο.
Έρευνες δείχνουν ότι η υπερβολική κατανάλωση αλκοόλ μπορεί να
οδηγήσει σε μια ποικιλία διαφορετικών καρκίνων, συμπεριλαμβανομένου του
στόματος, του οισοφάγου, του λάρυγγα, του ήπατος, και του μαστού. Μπορεί
επίσης να προκαλέσει σοβαρές βλάβες σε όλα σχεδόν τα βασικά όργανα του
σώματος.
Καρδιά
Με την πάροδο του χρόνου, η υπερβολική κατανάλωση αλκοόλ αρχίζει να
εξασθενεί τον καρδιακό μυ με αποτέλεσμα να υπάρχει ανωμαλία στην ροή του
αίματος. Οι αλκοολικοί συχνά πάσχουν από μια κατάσταση γνωστή ως
μυοκαρδιοπάθεια. Οι άνθρωποι, οι οποίοι διαγιγνώσκονται με
μυοκαρδιοπάθεια που προκαλείται από το αλκοόλ, τείνουν να αντιμετωπίζουν
δυσκολία στην αναπνοή, αρρυθμία (ανώμαλος καρδιακός ρυθμός), κόπωση,
διόγκωση του ήπατος, και επίμονο βήχα. Το αλκοόλ μπορεί επίσης να
αυξήσει τον κίνδυνο για καρδιακή προσβολή, εγκεφαλικό επεισόδιο και
υπέρταση.
Εγκέφαλος
 Επιβραδύνοντας την αναμετάδοση πληροφοριών μεταξύ των
νευροδιαβιβαστών, η αιθανόλη που περιέχουν τα αλκοολούχα ποτά μπορεί να
προκαλέσει βλάβη σε πολλές περιοχές του εγκεφάλου. Η παρατεταμένη βλάβη
στους νευροδιαβιβαστές του εγκεφάλου μπορεί να οδηγήσει σε απότομες
αλλαγές συμπεριφοράς και διάθεσης όπως κατάθλιψη, άγχος, απώλεια μνήμης,
και επιληπτικές κρίσεις. Ο αλκοολισμός σε συνδυασμό με την κακή
διατροφή μπορεί επίσης να προκαλέσει το σύνδρομο Wernicke-Korsakoff.
Συκώτι
Όπως προαναφέρθηκε, το συκώτι είναι από τα όργανα του σώματος που
πλήττεται πιο σοβαρά από κάθε άλλο. Το συκώτι μας είναι απαραίτητο για
τη σωστή πέψη της τροφής, την απορρόφηση θρεπτικών συστατικών, τον
έλεγχο των λοιμώξεων, και για την αποτοξίνωση του σώματος. Η κίρρωση του
ήπατος είναι η αιτία ανάγκης μεταμόσχευσης στο 48,2% των ασθενών που
χρειάζονται μεταμόσχευση ήπατος.
Πάγκρεας
Εκτός από το ήπαρ, το αλκοόλ είναι επιβλαβές και για το πάγκρεας
επειδή το αναγκάζει να παράγει ένζυμα στο εσωτερικό του, αντί να τα
στέλνει στο λεπτό έντερο. Η συσσώρευση αυτή των ενζύμων στο πάγκρεας
οδηγεί στη φλεγμονή, η οποία είναι γνωστή και ως παγκρεατίτιδα. Τα
συμπτώματα της οξείας παγκρεατίτιδας είναι κοιλιακό άλγος, ναυτία ή
έμετος, αύξηση του καρδιακού ρυθμού, διάρροια και πυρετός, ενώ η χρόνια
παγκρεατίτιδα οδηγεί σε διαβήτη, ακόμα και σε θάνατο.
Νεφρά
Λόγω της διουρητικής δράσης που έχει, το αλκοόλ προκαλεί αύξηση της
ποσότητας των ούρων που παράγει το σώμα. Τα νεφρά δεν είναι σε θέση να
ρυθμίσουν την ποσότητα των ούρων και των υγρών του σώματος,
συμπεριλαμβανομένης της κατανομής του νατρίου, του καλίου και των ιόντων
χλωρίου. Αυτό μπορεί με τη σειρά του να διαταράξει την ισορροπία των
ηλεκτρολυτών στον οργανισμό μας. Η υπερβολική κατανάλωση αλκοόλ μπορεί
επίσης να οδηγήσει σε υψηλή αρτηριακή πίεση, η οποία είναι η δεύτερη
κύρια αιτία της νεφρικής ανεπάρκειας.
Επιβραδύνοντας την αναμετάδοση πληροφοριών μεταξύ των
νευροδιαβιβαστών, η αιθανόλη που περιέχουν τα αλκοολούχα ποτά μπορεί να
προκαλέσει βλάβη σε πολλές περιοχές του εγκεφάλου. Η παρατεταμένη βλάβη
στους νευροδιαβιβαστές του εγκεφάλου μπορεί να οδηγήσει σε απότομες
αλλαγές συμπεριφοράς και διάθεσης όπως κατάθλιψη, άγχος, απώλεια μνήμης,
και επιληπτικές κρίσεις. Ο αλκοολισμός σε συνδυασμό με την κακή
διατροφή μπορεί επίσης να προκαλέσει το σύνδρομο Wernicke-Korsakoff.
Συκώτι
Όπως προαναφέρθηκε, το συκώτι είναι από τα όργανα του σώματος που
πλήττεται πιο σοβαρά από κάθε άλλο. Το συκώτι μας είναι απαραίτητο για
τη σωστή πέψη της τροφής, την απορρόφηση θρεπτικών συστατικών, τον
έλεγχο των λοιμώξεων, και για την αποτοξίνωση του σώματος. Η κίρρωση του
ήπατος είναι η αιτία ανάγκης μεταμόσχευσης στο 48,2% των ασθενών που
χρειάζονται μεταμόσχευση ήπατος.
Πάγκρεας
Εκτός από το ήπαρ, το αλκοόλ είναι επιβλαβές και για το πάγκρεας
επειδή το αναγκάζει να παράγει ένζυμα στο εσωτερικό του, αντί να τα
στέλνει στο λεπτό έντερο. Η συσσώρευση αυτή των ενζύμων στο πάγκρεας
οδηγεί στη φλεγμονή, η οποία είναι γνωστή και ως παγκρεατίτιδα. Τα
συμπτώματα της οξείας παγκρεατίτιδας είναι κοιλιακό άλγος, ναυτία ή
έμετος, αύξηση του καρδιακού ρυθμού, διάρροια και πυρετός, ενώ η χρόνια
παγκρεατίτιδα οδηγεί σε διαβήτη, ακόμα και σε θάνατο.
Νεφρά
Λόγω της διουρητικής δράσης που έχει, το αλκοόλ προκαλεί αύξηση της
ποσότητας των ούρων που παράγει το σώμα. Τα νεφρά δεν είναι σε θέση να
ρυθμίσουν την ποσότητα των ούρων και των υγρών του σώματος,
συμπεριλαμβανομένης της κατανομής του νατρίου, του καλίου και των ιόντων
χλωρίου. Αυτό μπορεί με τη σειρά του να διαταράξει την ισορροπία των
ηλεκτρολυτών στον οργανισμό μας. Η υπερβολική κατανάλωση αλκοόλ μπορεί
επίσης να οδηγήσει σε υψηλή αρτηριακή πίεση, η οποία είναι η δεύτερη
κύρια αιτία της νεφρικής ανεπάρκειας.
Straight to Your Head
Thirty seconds
after your first sip, alcohol races into your brain. It slows down the
chemicals and pathways that your brain cells use to send messages. That
alters your mood, slows your reflexes, and throws off your balance. You
also can’t think straight, which you may not recall later, because
you’ll struggle to store things in long-term memory.
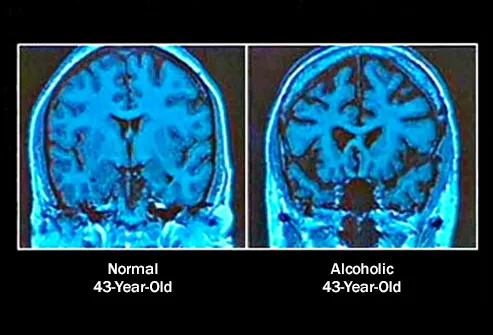
Your Brain Shrinks
If you drink
heavily for a long time, booze can affect how your brain looks and
works. Its cells start to change and even get smaller. Too much alcohol
can actually shrink your brain. And that’ll have big effects on your
ability to think, learn, and remember things. It can also make it harder
to keep a steady body temperature and control your movements.
Does It Help You Sleep?
Alcohol’s slow-down
effect on your brain can make you drowsy, so you may doze off more
easily. But you won’t sleep well. Your body processes alcohol throughout
the night. Once the effects wear off, it leaves you tossing and
turning. You don’t get that good REM sleep your body needs to feel
restored. And you’re more likely to have nightmares and vivid dreams.
You’ll also probably wake up more often for trips to the bathroom.
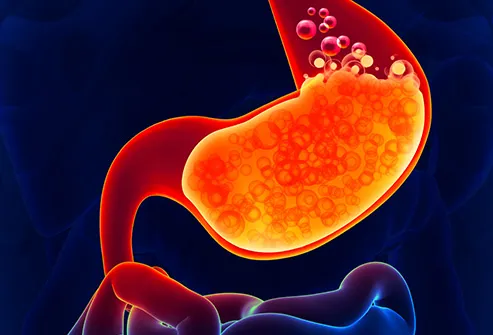
More Stomach Acid
Booze irritates the
lining of your stomach and makes your digestive juices flow. When
enough acid and alcohol build up, you get nauseated and you may throw
up. Years of heavy drinking can cause painful sores called ulcers in
your stomach. And high levels of stomach juices mean you won’t feel
hungry. That’s one reason long-term drinkers often don’t get all the
nutrients they need.
Diarrhea and Heartburn
Your small
intestine and colon get irritated, too. Alcohol throws off the normal
speed that food moves through them. That’s why hard drinking can lead to
diarrhea, which can turn into a long-term problem. It also makes
heartburn more likely – it relaxes the muscle that keeps acid out of
your esophagus, the tube that connects your mouth and stomach.
Why You Have to Pee … Again
Your brain gives
off a hormone that keeps your kidneys from making too much urine. But
when alcohol swings into action, it tells your brain to hold off. That
means you have to go more often, which can leave you dehydrated. When
you drink heavily for years, that extra workload and the toxic effects
of alcohol can wear your kidneys down.
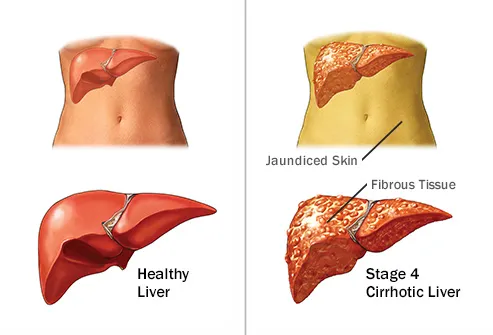
The Steps to Liver Disease
Your liver breaks
down almost all the alcohol you drink. In the process, it handles a lot
of toxins. Over time, heavy drinking makes the organ fatty and lets
thicker, fibrous tissue build up. That limits blood flow, so liver cells
don’t get what they need to survive. As they die off, the liver gets
scars and stops working as well, a disease called cirrhosis.
Pancreas Damage and Diabetes
Normally, this
organ makes insulin and other chemicals that help your intestines break
down food. But alcohol jams that process up. The chemicals stay inside
the pancreas. Along with toxins from alcohol, they cause inflammation in
the organ, which can lead to serious damage. After years, that means
you won’t be able to make the insulin you need, which can lead to
diabetes. It also makes you more likely to get pancreatic cancer.
What’s a Hangover?
That
cotton-mouthed, bleary-eyed morning-after is no accident. Alcohol makes
you dehydrated and makes blood vessels in your body and brain expand.
That gives you your headache. Your stomach wants to get rid of the
toxins and acid that booze churns up, which gives you nausea and
vomiting. And because your liver was so busy processing alcohol, it
didn’t release enough sugar into your blood, bringing on weakness and
the shakes.
An Offbeat Heart
One night of binge
drinking can jumble the electrical signals that keep your heart’s rhythm
steady. If you do it for years, you can make those changes permanent.
And, alcohol can literally wear your heart out. Over time, it causes
heart muscles to droop and stretch, like an old rubber band. It can’t
pump blood as well, and that impacts every part of your body.
A Change in Body Temperature
Alcohol widens your
blood vessels, making more blood flow to your skin. That makes you
blush and feel warm and toasty. But not for long. The heat from that
extra blood passes right out of your body, causing your temperature to
drop. On the other hand, long-term, heavy drinking boosts your blood
pressure. It makes your body release stress hormones that narrow blood
vessels, so your heart has to pump harder to push blood through.
A Weaker Immune System
You might not link a
cold with a night of drinking, but there might be a connection. Alcohol
puts the brakes on your immune system. Your body can’t make the numbers
of white blood cells it needs to fight germs. So for 24 hours after
drinking, you’re more likely to get sick. Long-term, heavy drinkers are
much more likely to get illnesses like pneumonia and tuberculosis.
Hormone Havoc
These powerful
chemicals manage everything from your sex drive to how fast you digest
food. To keep it all going smoothly, you need them in the right balance.
But alcohol throws them out of whack. In women, that can knock your
periods off cycle and cause problems getting pregnant. In men, it can
mean trouble getting an erection, a lower sperm count, shrinking
testicles, and breast growth.
Hearing Loss
Alcohol impacts
your hearing, but no one’s sure exactly how. It could be that it messes
with the part of your brain that processes sound. Or it might damage the
nerves and tiny hairs in your inner ear that help you hear. However it
happens, drinking means you need a sound to be louder so you can hear
it. And that can become permanent. Long-term drinkers often have hearing
loss.
Thin Bones, Less Muscle
Heavy drinking can
throw off your calcium levels. Along with the hormone changes that
alcohol triggers, that can keep your body from building new bone. They
get thinner and more fragile, a condition called osteoporosis. Booze
also limits blood flow to your muscles and gets in the way of the
proteins that build them up. Over time, you’ll have lower muscle mass
and less strength.
SOURCES : WebMD , ONMED .GR etc
 Επιβραδύνοντας την αναμετάδοση πληροφοριών μεταξύ των
νευροδιαβιβαστών, η αιθανόλη που περιέχουν τα αλκοολούχα ποτά μπορεί να
προκαλέσει βλάβη σε πολλές περιοχές του εγκεφάλου. Η παρατεταμένη βλάβη
στους νευροδιαβιβαστές του εγκεφάλου μπορεί να οδηγήσει σε απότομες
αλλαγές συμπεριφοράς και διάθεσης όπως κατάθλιψη, άγχος, απώλεια μνήμης,
και επιληπτικές κρίσεις. Ο αλκοολισμός σε συνδυασμό με την κακή
διατροφή μπορεί επίσης να προκαλέσει το σύνδρομο Wernicke-Korsakoff.
Επιβραδύνοντας την αναμετάδοση πληροφοριών μεταξύ των
νευροδιαβιβαστών, η αιθανόλη που περιέχουν τα αλκοολούχα ποτά μπορεί να
προκαλέσει βλάβη σε πολλές περιοχές του εγκεφάλου. Η παρατεταμένη βλάβη
στους νευροδιαβιβαστές του εγκεφάλου μπορεί να οδηγήσει σε απότομες
αλλαγές συμπεριφοράς και διάθεσης όπως κατάθλιψη, άγχος, απώλεια μνήμης,
και επιληπτικές κρίσεις. Ο αλκοολισμός σε συνδυασμό με την κακή
διατροφή μπορεί επίσης να προκαλέσει το σύνδρομο Wernicke-Korsakoff.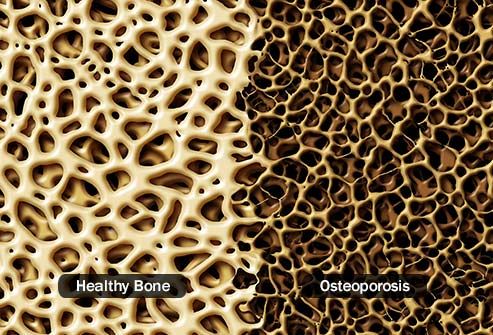

















Δεν υπάρχουν σχόλια:
Δημοσίευση σχολίου