Αντιισταμινικά και αλλεργίες
Οι αλλεργίες της άνοιξης είναι ήδη εδώ και λίγο καιρό και ίσως γίνουν ακόμα πιο έντονες . Έτσι, ολοένα και περισσότεροι άνθρωποι προσφεύγουν στα αντιισταμινικά φάρμακα, για να προλάβουν ή/και να θεραπεύσουν τα συμπτώματα των αλλεργιών.Τα αντιισταμινικά είναι γενικώς πιο αποτελεσματικά, όταν λαμβάνονται τακτικά παρά κατά διαστήματα. Αυτό ισχύει ιδιαίτερα για τα άτομα με αλλεργική ρινίτιδα. Κατά τους θερινούς μήνες, η ποσότητα γύρης είναι γενικά υψηλότερη, άρα και η επαφή με το αλλεργιογόνο είναι συνεχής.Τα αντιισταμινικά φάρμακα χρησιμοποιούνται κυρίως για την θεραπεία της αλλεργικής ρινίτιδας, του κνησμού και για την αντιμετώπιση των τσιμπημάτων από έντομα.Μπορούν να χρησιμοποιηθούν, για να βοηθήσουν τη μείωση του αισθήματος αδιαθεσίας, ναυτίας, ή εμετού. Επίσης, δρουν άμεσα στην θεραπεία μιας σοβαρής αλλεργικής αντίδρασης που προκαλεί αναφυλαξία.Οι συχνότερες παρενέργειες είναι συνήθως ήπιες.Ένα αντιισταμινικό δισκίο ή σιρόπι συνήθως αρχίζει να δρα μέσα σε 30 λεπτά. Η αποτελεσματικότητα του κορυφώνεται μέσα σε 1-2 ώρες.Η τακτική και σωστή χρήση των αντιϊσταμινικών θα διατηρήσει τα συμπτώματά υπό έλεγχο. Η διάρκεια επίσης, της αγωγής θα εξαρτηθεί από τη επιμονή των συμπτωμάτων και βέβαια από τους ερεθιστικούς παράγοντες.
Οι περισσότεροι άνθρωποι μπορούν να πάρουν αντιισταμινικά με ασφάλεια. Τα αντιισταμινικά δεν πρέπει να χρησιμοποιούνται από άτομα με μια σπάνια μεταβολική διαταραχή που λέγεται οξεία πορφυρία. Επιπλέον, μπορεί να μην είναι κατάλληλο για άτομα με προβλήματα στο συκώτι ή τα νεφρά ή για εγκύους και θηλάζουσες μητέρες. Μπορούν επίσης να μην είναι κατάλληλα για άτομα με αυξημένη οφθαλμική πίεση . Πρίν απο την χρήση οποιουδήποτε φαρμάκου είναι σωστό να συμβουλεύεστε τον γιατρό σας και το ίδιο φυσικά ισχύει και για τα αντιισταμινικά.
Before taking an antihistamine, you should know:
- how to take it – including whether it needs to be taken with water or food, or how to use it correctly (if eye drops or a nasal spray)
- how much to take (the dose) – this can vary depending on things such as your age and weight
- when to take it – including how many times a day you can take it and when to take it (older types should be taken before bedtime)
- how long to take it for – some types can be used for a long time, but some are only recommended for a few days
- what to do if you miss a dose or take too much (overdose)
Side effects of antihistamines
Like all medicines, antihistamines can cause side effects.Side effects of older types of antihistamines can include:
- sleepiness (drowsiness) and reduced co-ordination, reaction speed and judgement – don't drive or use machinery after taking these antihistamines because of this risk
- dry mouth
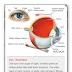
- blurred vision
- difficulty emptying your bladder
- headache
- dry mouth
- feeling sick
- drowsiness – this is less common than with older types of antihistamines
Taking antihistamines with other medicines, food or alcohol
Speak to a pharmacist or your GP before taking antihistamines if you're already taking other medicines.There may be a risk the medicines could affect each other, which could stop either from working properly or increase the risk of side effects.
Examples of medicines that could cause problems if taken with antihistamines include some types of:
- antidepressants
- stomach ulcer or gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) medicines
- cough and cold remedies that also contain an antihistamine
Food and other drinks don't affect most antihistamines, but check the leaflet that comes with your medicine to make sure.
Who can take antihistamines
Most people can safely take antihistamines.But speak to a pharmacist or your GP for advice if you:
- are pregnant
- are breastfeeding
- are looking for a medicine for a young child
- are taking other medicines – read about taking antihistamines with other medicines
- have an underlying condition, such as heart disease, liver disease, kidney disease or epilepsy
recommend one that's best for you.
Always read the leaflet that comes with your medicine to check it's safe for you before taking it or giving it to your child.












Δεν υπάρχουν σχόλια:
Δημοσίευση σχολίου